Key Factors to Differentiate Cat5 vs Cat5e vs Cat6 vs Cat7 vs Cat8
- Bandwidth: Normally, if a cable has a higher frequency of MHz, the transmission speed is more efficient.
- Speed: The speed of transmission changes according to the category, which determines the effectiveness of the cable.
- Crosstalk: The “bleeding” of signals between one cable into another due to “induction” will result in slow network transfer speeds, and even block the transfer of signals over the cable.
| Category | Max Transmission Speed (At 100 Meters) | Max Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|
| Cat 5 | 10/100 Mbps | 100 MHz |
| Cat 5e | 1000 Mbps / 1 Gbps | 100 MHz |
| Cat 6 | 1000 Mbps / 1 Gbps | 250 MHz |
| Cat 6a | 10000 Mbps / 10 Gbps | 500 MHz |
| Cat 7 | 10000 Mbps / 10 Gbps | 600 MHz |
| Cat 8 | 25 Gbps or 40Gbps | 2000 MHz at 30 meters |
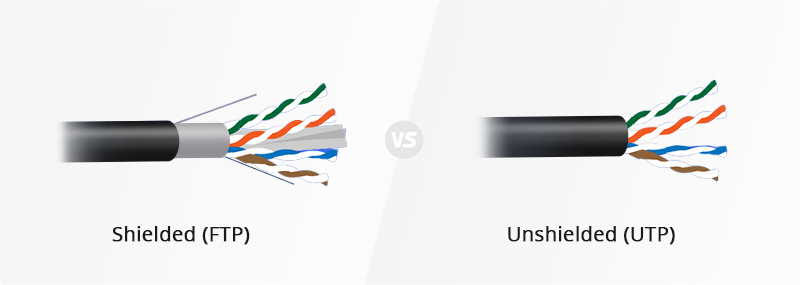
Shielding Type of Ethernet Cables Plus Their Applications
Before knowing the shielding type of Ethernet cables, it is suggested to be familiar with the shielding code in advance.
“TP” stands for “Twisted Pair”
“U” stands for “Unshielded or Unscreened”
“F” stands for “Foil Shielding”
“S” stands for “Braided Shielding”
“A” stands for “Armour”
The shielding type of Ethernet cables and their applications are as follows:
| Shielding Type | Applications |
|---|---|
| STP | Suitable for high-speed network and high security transmission. |
| SFTP | The low attenuation of internal signal making it nice for special environment of professional wiring. |
| UTP | Suited for network applications with transmission bandwidth less than 250MHz and no special performance requirements. |
| FTP | Designed to provide the assembly with greater protection from crosstalk from adjacent pairs and other cables, RFI and EMI. |
| ASTP | Perfect opt for preventing rodent damage, also nice for explosion-proof wiring system. |
 汉信
汉信

