According to the frequency and signal-to-noise ratio, the twisted pair network cable can be divided into Cat 3, Cat 4, Cat 5, Cat 5e, Cat 6, Cat 6a, Cat 7, Cat 7a and Cat 8 Ethernet/copper cables. Cat is standard for Category, all of them are applied for short distance transmission. The detailed specifications of twisted pair network cable types are listed in the below chart.
| Category | Typical Construction | Max Bandwidth | Transmission Speeds | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat 3 | UTP | 16 MHz | 10Mbps | 10BASE-T and 100BASE-T4 Ethernet |
| Cat 4 | UTP | 20 MHz | 16Mbps | 16Mbit/s Token Ring |
| Cat 5 | UTP | 100 MHz | 10-100Mbps | 100BASE-TX & 1000BASE-T Ethernet |
| Cat 5e | UTP | 100 MHz | 1000Mbps-1Gbps | 100BASE-TX & 1000BASE-T Ethernet |
| Cat 6 | STP | 250 MHz | 10Gbps (55m) | 10GBASE-T Ethernet |
| Cat 6a | STP | 500 MHz | 10Gbps (55m) | 10GBASE-T Ethernet |
| Cat 7 | STP | 600 MHz | 100Gbps (15m) | 10GBASE-T Ethernet or POTS/CATV/1000BASE-T over single cable |
| Cat 7a | STP | 1000 MHz | 100Gbps (15m) | 10GBASE-T Ethernet or POTS/CATV/1000BASE-T over single cable |
| Cat 7a | STP | 2000 MHz | 4Gbps (30m) | 40GBASE-T Ethernet or POTS/CATV/1000BASE-T over single cable |
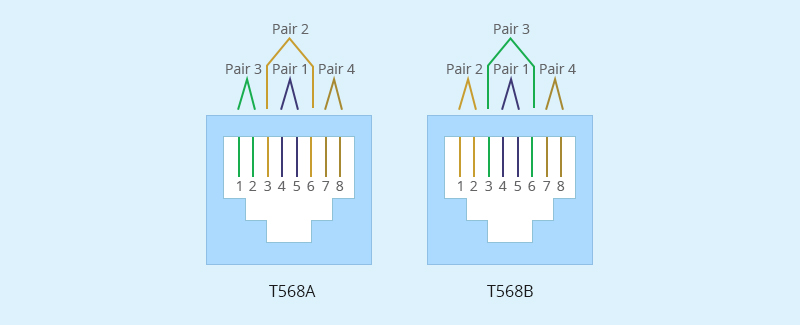
T568A and T568B are two basic wiring standards that are used by twisted pair network cables. They are telecommunications standards from TIA and EIA that specify the pin arrangements for connectors (often RJ45) on UTP or STP network cables. The number 568 refers to the order in which wires within the twisted pair cables are terminated and attached to the connector. The only difference between T568A and T568B is that the orange and green pairs are interchanged (see the figure below).
 汉信
汉信

