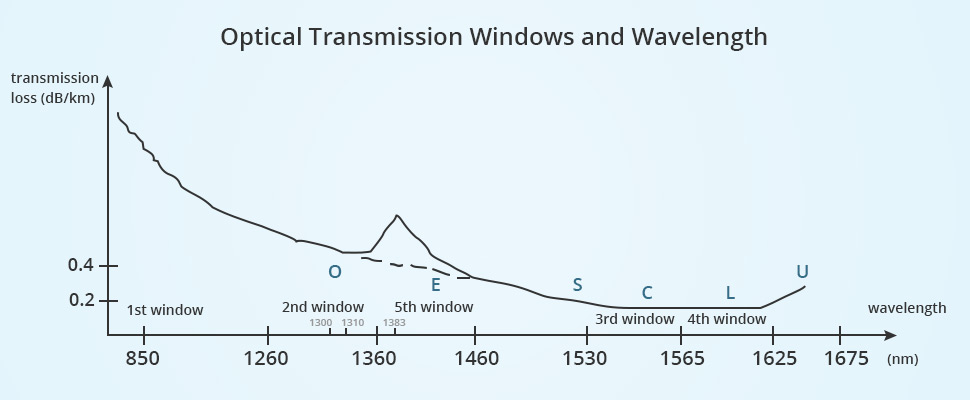
In May 2002, the ITU-T organization divided the fiber optical communication system into six bands as O, E, S, C, L and U6. Multi-mode optical fiber at 850nm is known as the first window, single-mode optical fiber at O band is referred to as the second band. C band is called as the third window, L band is the forth window and E band is the fifth window. The following table shows the wavelength bands for both multimode fiber optic cable and single-mode fiber optic cable.
| Frequency band | Window | Wavelength range (nm) | Frequency range (THz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| / | 1 | 850(770-910) | / |
| Original band | 2 | 1260-1360 | 237.9-220.4 |
| Extended band | 5 | 1360-1460 | 220.4-205.3 |
| Short wavelength band | / | 1460-1530 | 205.3-195.9 |
| Conventional band | 3 | 1530-1565 | 195.9-191.6 |
| Longer wavelength band | 4 | 1565-1625 | 191.6-184.5 |
| Ultralength wavelength band | / | 1625-1675 | 184.5-179.0 |
The frequency range in the table above refers to the frequency of light. According to the formula speed = wavelength x frequency, we can easily figure out the frequency of light. Its relation to the transmission loss of fiber optic cable and wavelength has been displayed as follow:
In the early days of fiber optic communication the LED was employed as a light source due to its low price. Multi-mode fiber optic cables that operate at 850nm and 1300nm became the first choice for building small network, while single-mode optical fiber cables, working at 1310nm and 1550nm with laser as the light source , were the foundation for constructing large network. If there were more windows available for single-mode optic cable, one fiber optic cable would achieve ultra high speed transmission by transmitting signals at different wavelength at the same time by employing WDM (wavelength division multiplexing) technology, thus maximizing the potential of single mode fiber. Telephone and network and be using at the same time via ADSL (asymmetric digital subscriber line) modem. That’s because voice and data use different frequency. And this principle is similar with WDM and ADSL technology, which are usually applied in main networks that require higher bandwidth.
 汉信
汉信

